Mobile Apps in Government: Adoption Trends & Service Impact
In an era where nearly 98% of Americans own a cellphone and 91% own a smartphone, government agencies are rapidly turning to mobile apps to meet people where they are on their mobile devices. Citizens today expect public services to be as convenient and user-friendly as private sector apps. Research confirms this shift: over 80% of residents now prefer using a mobile app to access government services and information. This demand is driving a new wave of digital innovation in the public sector. Once a novelty, mobile apps for digital government have become essential tools for modernizing service delivery and engaging digital citizens. In this article, we explore the current government mobile app trends, their impact on public services, and what they mean for the future of digital governance.
The Rise of Mobile Apps in Government
- Citizen Expectations Are Mobile-First: The public’s preference for mobile access is clear. A recent survey found 70% of citizens would prefer to interact with local governments through a mobile app rather than traditional methods. Another analysis by the National League of Cities put the figure even higher over 80% favor mobile apps for government services. This overwhelming majority reflects how everyday life has gone mobile. People spend about 87% of their mobile device time using apps (as opposed to web browsers), so they naturally gravitate to apps for services. Governments that embrace mobile apps are tapping into the benefits of mobile apps for digital communities, making public services more accessible and convenient.
- Widespread Adoption by Agencies: In response, many government bodies have launched their own apps. As of 2023, over 60% of U.S. local authorities have adopted dedicated mobile applications for citizen services, collectively serving more than 100 million. At the federal level, digital initiatives are also accelerating. For example, the U.S. Digital Service reported enabling 18.25 million veterans to access health and benefits via new mobile-friendly tools, vastly expanding reach. Across government, what began as a slow trickle of pilot projects a decade ago is now a mainstream movement. Mobile app development government agencies undertake is no longer experimental it’s becoming standard practice for delivering information and services.
- Mobile Traffic Overtaking Desktop: The growth of government mobile apps parallels a broader trend: more citizens now reach public services via mobile devices than desktop computers. Over the past decade, mobile web traffic to U.S. government sites skyrocketed from just 13% of visitors in 2013 to about 58% of all visitors in 2023, overtaking desktop usage. Desktop access to government websites fell from 80% down to 40% in the same period.
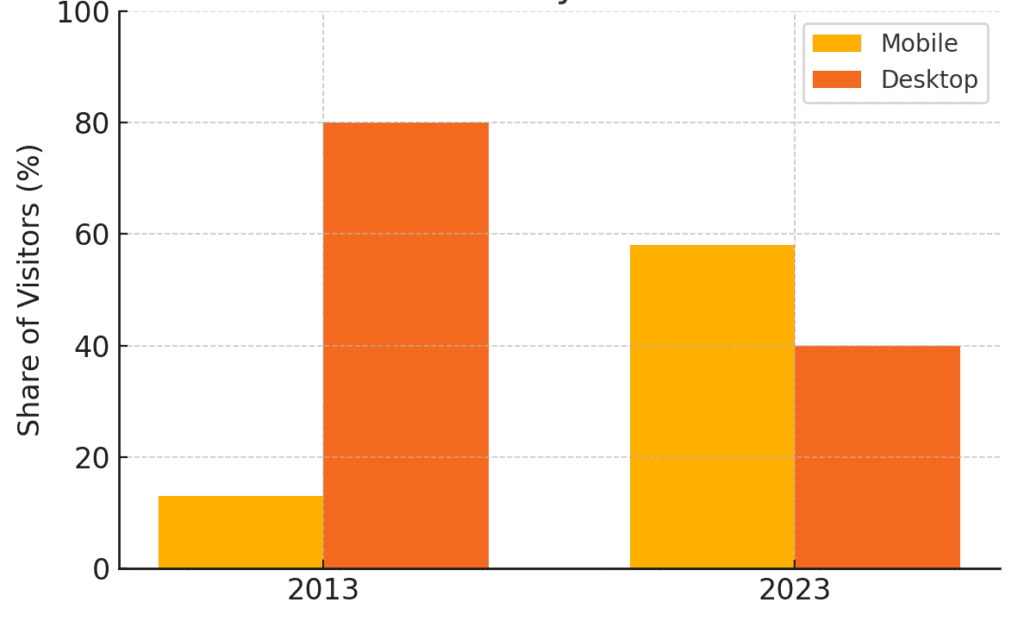
- Mobile vs. Desktop Visitors on U.S. Government Websites (2013 vs 2023). Mobile usage (blue) has surged, surpassing desktop (orange) by 2023. This surge in mobile activity underscores why agencies are investing in native apps: citizens are already on mobile, and they expect government services to be optimized for it. In short, mobile is now the default gateway to digital government.
- Global Trend, Not Just Local: The shift to mobile government is a worldwide phenomenon. According to a United Nations survey, 70% of countries now offer some form of mobile health services for their citizens, 66% use mobile apps or SMS for public education updates, and 53% provide environment and sustainability info via mobile channels.
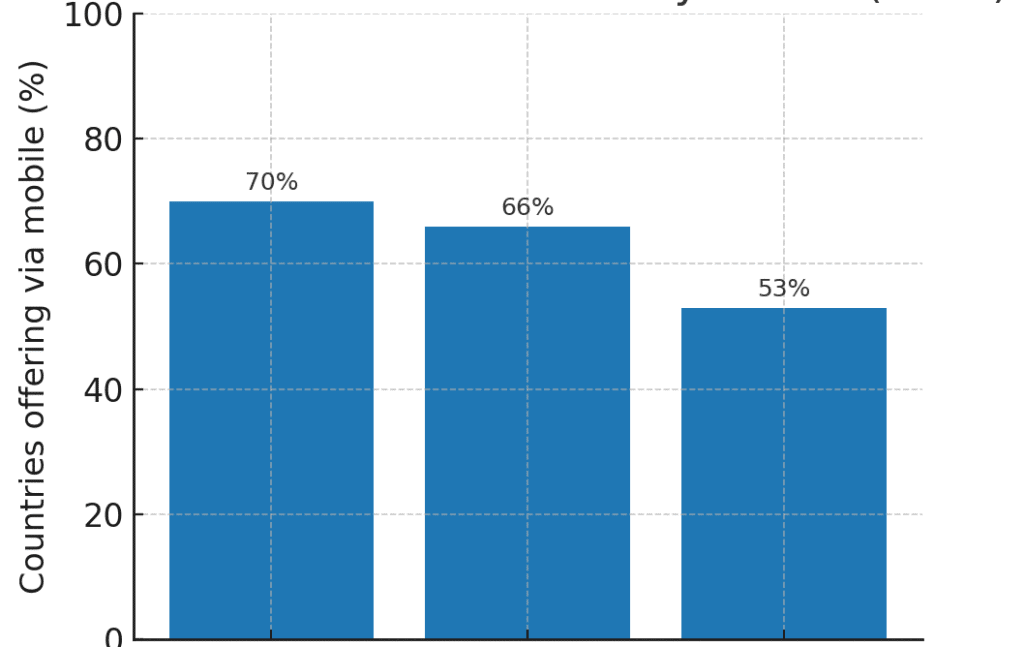
Global adoption of mobile government services by sector (percentage of countries offering each, per U.N. survey). From smart city apps in Seoul to national COVID alert apps in Europe, mobile platforms are becoming integral to government service delivery across the globe. These mobile apps for digital government initiatives are recognized as key enablers of accessible, inclusive public services in the digital age.
Service Impact: Benefits and Outcomes
Governments that implement mobile apps are seeing significant improvements in service delivery and citizen satisfaction. The benefits of government mobile app adoption can be measured across multiple metrics:
- Higher Citizen Satisfaction: Well-designed government apps can dramatically improve public sentiment. In one city, citizen satisfaction scores jumped 72% after launching a new service app. Residents feel heard and helped when they can accomplish tasks through an easy mobile interface instead of standing in line or navigating clunky websites. In fact, people now expect government services to be as seamless as online shopping and when agencies deliver, approval ratings rise accordingly. Offering mobile self-service options signals that the government is listening to constituents needs. It’s no surprise that a majority of residents see such apps as a sign of a smart, responsive government.
- Faster Response Times: Mobile apps streamline how citizens request services and how staff respond. Research shows that cities using apps for 311 service requests achieved about a 25% reduction in response times on average. Issues reported through an app (with photos and GPS location) can be routed instantly to the right department, skipping paperwork and phone tag. Some communities have reported even bigger gains for instance, Boston’s 311 app led to a 40% faster resolution of non-emergency issues in its first year. Quicker fixes for potholes, trash pickup, and repairs mean a higher quality of life for residents. Speedier service is one of the clear benefits of mobile apps for digital communities, building trust that local government can respond in real time.
- Operational Efficiency & Cost Savings: On the back-end, government apps drive internal efficiencies. By digitizing formerly manual processes, apps help staff do more with less. One analysis found a 32% drop in administrative costs after a city implemented mobile apps for common tasks. Automating bill payments, permit renewals, and incident reporting through an app cuts down on paper processing and data re-entry, saving valuable staff hours. Likewise, employees in the field become more productive: one report noted a 75% increase in internal staff efficiency when governments adopted mobile task-management apps for their workforce. In short, the same tax dollars deliver more when processes are app-powered. Over time, these efficiency gains free up budget and personnel for higher-value initiatives.
- Broader Engagement & Inclusivity: A well-designed app can broaden access to services across demographics. 60% of seniors (65+) now use mobile apps, debunking the myth that only young people go digital. From tech-savvy teens to retirees, all age groups appreciate the convenience of tapping a phone rather than waiting on hold. Mobile apps also help bridge the digital divide. Many lower-income households rely on smartphones as their only internet connection. By offering services through apps, governments ensure underserved residents can pay bills, get alerts, and request assistance from their pocket devices just like everyone else. In this way, apps meet people of all ages and backgrounds where they are increasing equity in access. Additionally, mobile apps enable real-time multilingual updates and accessible interfaces that can be more user-friendly than complex web portals, further expanding inclusion.
- Stronger Communication Channels: Mobile apps open direct, instant communication between agencies and the public. Push notifications from government apps boast an open rate around 90%, far higher than email or even text message alerts. This means important updates (road closures, weather warnings, public health advisories) are more likely to be seen by residents. In a survey, 84% of citizens said they want real-time emergency alerts and notifications from their local government a demand that apps are ideally suited to fulfill. Residents can also use app features to quickly report issues (with photos/GPS) and know their report is logged and tracked. This two-way communication loop wasn’t possible at scale with older channels. The result is a more informed public and a more transparent government. Citizens feel connected and safer when they receive timely alerts and see that their inputs lead to action.
These outcomes illustrate why investing in mobile apps is yielding such high returns for public-sector organizations. From benefits of government mobile app adoption like happier constituents and lower costs, to intangible gains in trust and transparency, the impact on services has been overwhelmingly positive. Governments that once struggled with clunky websites and slow paper workflows are now leveraging app technology to become more agile, responsive, and citizen-centric.
Key Challenges and Considerations
While the case for government mobile apps is compelling, agencies must navigate several challenges to fully realize these benefits. Developing and deploying an app in the public sector comes with unique considerations:
Integration with Legacy Systems:
Governments rarely start from scratch they have existing databases and software for various services. A new app must integrate with these local government software systems (for permitting, 311 case management, billing, etc.) to be truly effective. In practice, this means using APIs and middleware to connect the app with back-end data in real time. When done right, an app can plug into legacy systems securely and pull together information from multiple departments. For example, a city app might tie into the GIS database to map issues reported by citizens. Ensuring smooth integration is critical; otherwise, the app could become a silo of data on its own. Many municipalities accelerate development by partnering with a specialized government app developer that knows how to bridge modern mobile interfaces with older government IT systems. Leveraging proven platforms and expert developers helps avoid reinventing the wheel and reduces deployment time.
Security and Privacy:
Ensuring robust application security for government apps is paramount. Public-sector apps often handle sensitive information from personal citizen data to payment transactions making them attractive targets for cyber threats. Agencies need to implement strong encryption, user authentication, and vulnerability testing for their apps, just as they do for websites. Alarmingly, a 2024 study found that 93% of organizations felt confident in their mobile app security, yet 62% had experienced a mobile breach in the past year. This gap highlights the importance of rigorous security measures and ongoing audits. Government apps must also adhere to privacy regulations and be transparent about data use. Users will only adopt apps if they trust them. Engaging a reputable government IT solutions provider or in-house cybersecurity team to conduct thorough security assessments is a smart step before launch. In addition, compliance with standards like ADA accessibility is now legally required for government websites and mobile apps. Agencies must build apps that are secure and accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.
User Experience and Adoption:
Simply launching an app doesn’t guarantee that citizens will use it. Governments need to invest in user experience (UX) design and outreach. Early municipal apps sometimes saw low adoption because they were unintuitive or failed to address real user needs. Modern best practices call for citizen-centric design involving residents in testing and focusing on top tasks people want to accomplish. Features like intuitive navigation, multilingual support, and fast loading times are crucial for engagement. Marketing the app to the community is also important (e.g. social media, city newsletters, QR codes at public offices). When Toronto first released its 311 app, officials found they had to actively promote it to drive downloads, even though the service itself was high-value. Offering exclusive features (like mobile-only alerts or easy bill pay) can incentivize residents to try the app. Governments should treat their apps as continually evolving products, using analytics and feedback to improve over time. Public sector app modernization isn’t just a one-time project it’s an ongoing process of updating features, content, and compatibility as technology and user expectations change.
Governance and Maintenance:
Another consideration is long-term maintenance. Mobile operating systems update frequently, and security threats evolve, so government apps require regular patches and updates. Agencies must budget and plan for the app’s lifecycle, not just the initial development. This is where working with an experienced government IT solutions provider or having a dedicated internal team pays off. Ongoing support agreements can ensure the app stays up-to-date with OS changes (iOS, Android updates), remains secure, and continues to integrate with any new internal systems. Additionally, clear governance on content management is needed who will update the app with the latest news or handle incoming service requests on the back-end? Successful deployments often designate an app manager or cross-department team to coordinate the app’s operation. By planning for maintenance, training staff, and allocating resources post-launch, agencies can avoid the launch and forget pitfall and keep their app useful for years to come.
In summary, adopting mobile apps in government requires more than just coding skills. It demands a strategic approach to mobile app development government bodies undertake, addressing security, integration, UX, and sustainability. When these challenges are met, the payoff in citizen satisfaction and efficiency is well worth it. Many public agencies mitigate risks by partnering with a government app developer or a trusted government IT solutions provider that understands compliance and can deliver a polished, secure product. With careful planning, even risk-averse public institutions are overcoming hurdles and successfully launching apps that residents embrace.
Future Outlook: Smart, Mobile-First Government
Mobile apps in government are not a passing trend they are paving the way for a more connected, smart public sector. Looking ahead, several smart government technology trends are emerging around mobile platforms:
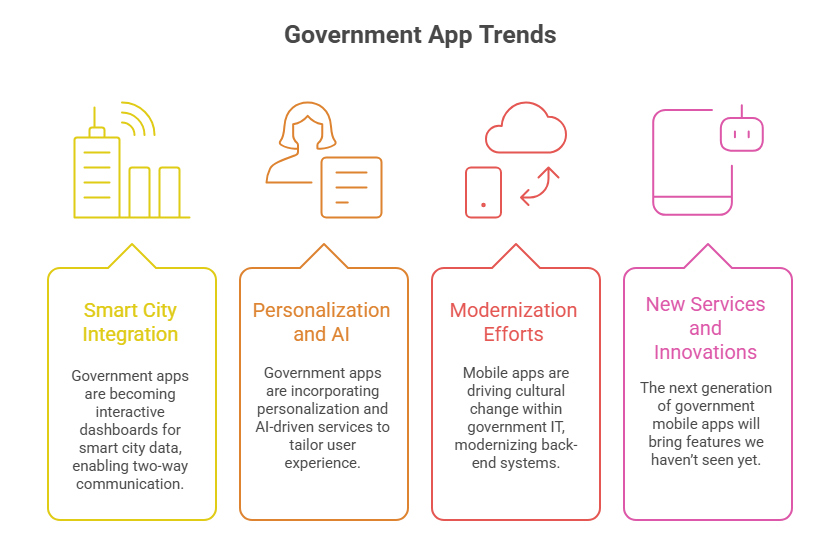
Deeper Smart City Integration:
Government apps are becoming the front-end for smart city systems. As cities deploy sensors and IoT devices for traffic, utilities, public safety, mobile apps serve as interactive dashboards to share that real-time data with citizens. For example, some city apps already show live public transit locations, available parking spots, or air quality readings pulled from sensor networks. Residents can both receive this information and contribute data (reporting issues, crowdsourced inputs) through the app, creating a two-way smart city communication loop. One analysis notes that mobile apps effectively let citizens “interact directly with city systems, making urban life more connected and efficient.” This aligns with broader smart government technology trends that emphasize using digital interfaces and data to improve quality of life. We can expect future government apps to integrate even more with technologies like autonomous vehicles updates, smart grid energy alerts, and citywide AI assistants, further blurring the line between digital and physical services.
Personalization and AI:
Just as private-sector apps have become more personalized, government apps are likely to incorporate personalization and even AI-driven services. Imagine an app that tailors its home screen based on a user’s profile for instance, a parent sees school announcements and park events, while a senior sees information on health services and tax reminders. Some municipalities are exploring AI chatbots within their apps to handle common questions or guide residents through transactions in a conversational way. Looking at industry research, Gartner found that cities using AI-based personalization in their digital services saw a 50% boost in user engagement. In the near future, your city app might proactively notify you about a license renewal or suggest community meetings based on your interests. This kind of user-centric approach could further increase adoption and satisfaction. Of course, it also requires careful handling of data and transparency to maintain trust.
Continued Modernization Efforts:
Importantly, mobile apps are driving a cultural change within government IT. Agencies are recognizing that to offer great mobile services, they must modernize back-end systems and break down silos. Analysts note that by 2025, updating legacy systems to cloud-based, mobile-first platforms is a critical priority for governments seeking to stay relevant. More than 70% of government CIOs globally say they plan to increase investments in citizen experience technologies like; mobile apps and digital portals by 2026. This means we’ll see continued funding and attention on public sector app modernization and digital transformation initiatives. Legacy databases and paper forms are gradually being replaced or integrated via APIs, enabling the seamless app experiences citizens expect. The trend also extends to inter-agency collaboration for example, state governments launching umbrella apps that let users access multiple department services in one place, or city and county apps sharing data. The long-term vision is a mobile-first government where most routine interactions paying taxes, renewing IDs, reporting issues can be handled via a quick app session, while in-person visits become the exception.
New Services and Innovations:
The next generation of government mobile apps will likely bring features we haven’t seen yet. Some possibilities on the horizon include augmented reality (AR) features (imagine pointing your phone at a street and seeing an overlay of city permit info or historical facts), integration with digital IDs and wallets for secure credentials, and greater use of video/live chat for virtual appointments with government staff. Public safety agencies are testing apps that can send personalized evacuation routes to residents during emergencies, based on their GPS location. Smart government technology trends also point toward more regional and community-driven apps for instance, apps that connect neighboring cities or rural areas to share resources and information. The concept of a digital twin of a city (a virtual model updated in real time) could be partially accessible through citizen apps, giving unprecedented transparency into how the city functions. In essence, mobile apps will continue to evolve from simple informational tools to comprehensive platforms for civic life.
Conclusion
Mobile apps are revolutionizing how government services are delivered and experienced. In just a few years, we’ve gone from clunky city websites and long lines at government offices to tapping an icon on our phones for immediate access to public services. The government mobile app trends highlighted here from widespread citizen adoption to measurable service improvements make it clear that mobile apps are now a cornerstone of digital government strategy. They offer a direct channel to citizens, meeting the public’s expectations for speed, convenience, and transparency. Governments implementing apps have reaped rewards in the form of higher satisfaction, greater efficiency, and more inclusive engagement. Crucially, these apps also position agencies for the future by enabling real-time communication and integrating with smart city infrastructure.
That said, success in this arena requires more than just technology it demands planning for security, accessibility, and integration. Agencies must remain vigilant about application security for government platforms and ensure every resident can benefit from the digital services on offer. By addressing these factors and embracing a culture of continuous improvement, public-sector leaders can fully unlock the benefits of mobile apps for their communities. Many are already doing so, often in partnership with expert developers, and the results speak for themselves.
For CIOs, CTOs, and public-sector decision-makers, the message is that mobile apps are not just an IT project they are a strategic asset in improving citizen experience. They enable mobile apps for digital government to truly transform service delivery and bridge the gap between citizens and the state. As we look ahead, mobile technology will only become more ingrained in government operations and smart city ecosystems. Those who invest in it now will set the foundation for responsive, data-driven, and citizen-centric governance in the years to come. In a world where almost everyone carries a supercomputer in their pocket, governments that seize the opportunity of mobile apps can create more connected, empowered and satisfied communities one tap at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current government mobile app trends?
Government mobile app trends show a strong shift toward mobile-first citizen services, real-time notifications, and self-service portals. Agencies are prioritizing accessibility, security, and integration with legacy systems to improve service delivery.
Why are mobile apps important for digital government?
Mobile apps for digital government allow agencies to meet citizens where they are—on smartphones. They improve service access, reduce administrative workload, and support faster communication between governments and communities.
What are the benefits of government mobile apps for citizens?
The benefits of government mobile app adoption include faster service requests, real-time alerts, improved transparency, and higher citizen satisfaction. Apps also increase accessibility for residents who rely on mobile devices as their primary internet access.
How do mobile apps support public sector digital transformation?
Mobile apps are a core part of public sector app modernization by replacing paper-based workflows and outdated portals. They integrate with existing systems while enabling smarter, data-driven government operations.
Can mobile apps integrate with existing government systems?
Modern government mobile apps are designed to integrate with local government software, CRMs, GIS platforms, and legacy databases using secure APIs. This ensures continuity while enabling innovation.
Who develops mobile apps for government agencies?
A specialized government app developer with public-sector experience is critical. App Maisters delivers mobile app development for government agencies with a focus on compliance, accessibility, and long-term scalability.
Do mobile apps improve community engagement in the public sector?
Yes. The benefits of mobile apps for digital communities include higher engagement, faster issue resolution, and two-way communication through notifications, reporting tools, and service tracking.
What certifications should a government mobile app development company have?
A qualified government IT solutions provider should follow standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 27001 for information security, WCAG accessibility guidelines, and relevant public-sector compliance requirements areas where App Maisters aligns strongly.