How AI Really Works: A Look Inside Its Algorithms
AI algorithms are the step-by-step instructions that enable computers to perform tasks requiring intelligence. In effect, an AI algorithm analyzes data to detect patterns, make predictions, and autonomously improve over time. Think of it as a recipe: given inputs (data), the algorithm follows a procedure and adjusts its ingredients (parameters) through training. Unlike traditional rule-based programs that follow fixed logic, modern AI algorithms learn from data and adapt. For example, a recommendation system learns your preferences by mining your history, while a voice assistant like Alexa gets better at understanding your speech after more interactions. In short, AI algorithms evolve through experience, improving accuracy on tasks that would normally need human intelligence.
AI algorithms can be visualized as complex networks of data processing steps (as above). Each node or layer applies mathematical operations like multiplication, addition or comparison to the input data. During training, the model adjusts its internal parameters so that data flowing through the network produces the correct output. In practice, data scientists begin with large datasets and let the algorithm recognize patterns for example, identifying which images contain a cat or which past invoices hint at fraud. Over time and with feedback, the AI refines its process: if its prediction is wrong, it tweaks its parameters and tries again. This loop of prediction and correction called iterative improvement is why AI systems can improve accuracy the more data they process. In essence, modern AI works by searching for patterns in data and optimizing its steps to minimize errors, all without being told exactly how to solve each problem.
What Are AI Algorithms?
At a basic level, an AI algorithm is a set of mathematical rules that tells a computer how to process information, learn from it, and reach conclusions. These algorithms range from simple decision trees to complex neural networks. For instance, a supervised learning algorithm might take past data labeled with outcomes and learn to classify new inputs (like sorting emails into “spam” or “not spam”). An unsupervised algorithm, by contrast, finds hidden structure in data without predefined labels (for example clustering citizens by travel patterns). Reinforcement algorithms learn by trial and error, receiving rewards or penalties for actions like training an autonomous drone to navigate to a target.
In practical terms, AI algorithms allow machines to tackle tasks normally reserved for humans. As one expert explains, AI algorithms are sets of instructions that tell artificial intelligence technology how to process information, react to data, and make decisions autonomously. This means AI can do everything from translating language to predicting weather all by applying mathematical operations to data inputs. The key difference from classical computing is that AI algorithms adapt: instead of rigid code, they adjust their own logic when exposed to new information. In summary, AI algorithms are the blueprints for intelligent behavior: programmable instructions designed to learn, recognize patterns, and continuously improve.
How Do AI Algorithms Work?
AI algorithms work by training on data and iteratively refining themselves. The process generally follows these steps:
- Collect and prepare data: High-quality, relevant datasets are fed into the algorithm. This could be images, text, sensor readings, or any information relevant to the task. (As the saying goes, “garbage in, garbage out” the input data must be accurate and well-labeled for the AI to learn properly.)
- Pattern recognition: The algorithm uses mathematical models to spot patterns or correlations in the data. For example, it may recognize shapes in images or key phrases in text. This is akin to how humans learn by observation: the AI “looks” at many examples until it finds what is common among them.
- Iterative learning: Each time the model makes a prediction, it checks against the true answer (if supervised) and adjusts its parameters to reduce error. In reinforcement learning, it receives rewards or penalties to reinforce good behavior. This loop repeats thousands of times until the model’s performance stabilizes.
- Autonomous decision-making: After training, the AI algorithm applies its learned rules to new data. It can now make predictions or decisions autonomously, often with high speed and accuracy. For example, once trained on medical scans, an algorithm can autonomously flag tumors in new scans; or once trained on past traffic data, it can predict congestion.
This cycle of learning is what makes AI dynamic. Salesforce notes that “AI algorithms adapt and improve with new data” they don’t just run one fixed procedure, but continuously update based on feedback. Over time, an AI system can even detect subtle trends humans might miss. For instance, Netflix’s recommendation AI refines suggestions based on your evolving preferences, and Google’s search algorithm constantly learns from what users click on. In summary, AI algorithms work by digesting data, extracting regularities, and using those learned rules to guide future decisions, all while constantly self-improving.
Types of AI Algorithms
There are many types of AI algorithms, each suited to different kinds of problems. Broadly, they fall into a few main categories:
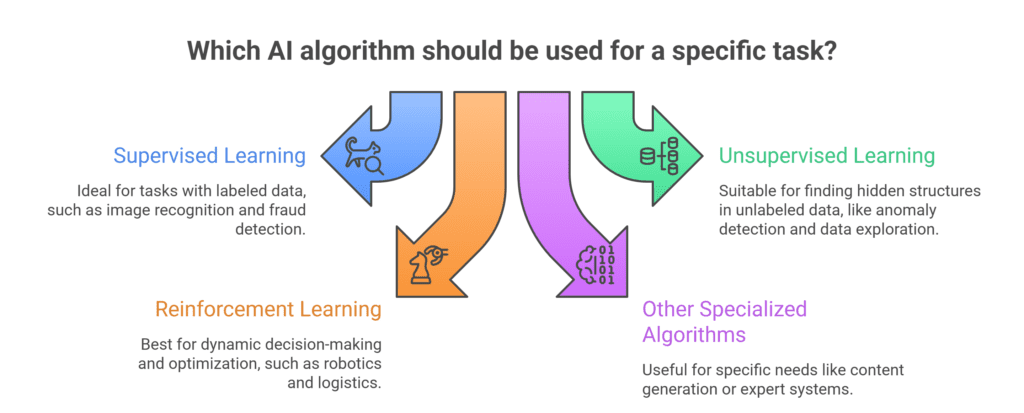
- Supervised learning algorithms: These learn from labeled data. For example, a supervised model might be trained on thousands of photos of animals, each tagged with the animal’s name. It uses that information to classify new images (e.g. “this photo is a cat”). Common techniques include decision trees, support vector machines, logistic regression, and neural networks. Supervised learning is widely used for tasks like image recognition, fraud detection, and sentiment analysis.
- Unsupervised learning algorithms: These handle unlabeled data, finding hidden structures or clusters. For example, they might group citizens into segments based on demographic or usage patterns without prior labels. Techniques like k-means clustering, principal component analysis, and autoencoders fall here. Governments use unsupervised AI for anomaly detection (flagging outliers in financial records) and data exploration.
- Reinforcement learning algorithms: These learn by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties. Think of training an agent to play chess: it makes moves, wins or loses points, and gradually learns which strategies maximize its score. Algorithms like Q-learning or policy gradient methods enable robotics, logistics optimization, and complex simulations.
- Other specialized algorithms: Beyond these main classes, there are many specific approaches. For instance, neural networks (including deep learning) mimic brain-like structures to learn complex functions. Genetic algorithms use evolutionary ideas to “breed” solutions. Generative models create new content (like images or text) by learning the data distribution. Rule-based expert systems encode human knowledge directly. Each type of algorithm has strengths depending on the problem (supervised methods excel when labeled data is abundant, while reinforcement is ideal for dynamic decision-making).
Understanding the types of AI algorithms is key to choosing the right tool. For example, a government traffic department might use a supervised neural network to classify incidents on camera feeds, whereas it might use unsupervised clustering to detect unusual patterns in crime statistics. By matching the method to the task, agencies can extract maximum value from their data.
Machine Learning for Government
Machine learning a subset of AI where algorithms learn from data is increasingly being adopted across Federal Government Agencies and other public entities. The goal is to harness vast amounts of government data for better decision-making and services. Machine learning can accelerate data analysis and insight generation. For instance, as IBM notes, ML helps agencies collect and analyze data more efficiently, offering actionable insights from the data they collect. This means AI can automate routine tasks (like processing forms) and surface trends (like detecting fraud patterns) far faster than manual methods.
Practical use cases abound. Agencies use machine learning to improve public safety and health: AI models scan satellite imagery to predict floods or wildfires, and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control uses ML to flag disease outbreak signals in health data. In finance, government auditors apply ML algorithms to spot anomalies in tax filings that might indicate identity theft or fraud. Even in law enforcement, pattern-recognition algorithms sift through surveillance footage to identify suspects (though with care to avoid bias). As one review highlights, machine learning and neural networks power computer vision systems for example, facial recognition or traffic monitoring by extracting patterns in images.
Machine learning is also enhancing citizen services. Modern smart city programs often feature AI-driven chatbots and automated citizen portals. For example, San Jose, California deployed an after-hours chatbot for government services: it provides 24/7 assistance in multiple languages to residents who cannot call during business hours. Similarly, Phoenix’s bilingual 311 portal uses an AI chatbot built on AWS Lex to answer common citizen questions around the clock. These chatbots reduce staff workload and ensure residents get timely help. In education, agencies might use ML to personalize learning materials; in welfare, they use it to predict which cases need urgent attention.
In short, machine learning for government helps turn data into better services. By applying the right algorithms, public agencies can automate manual processes (like document review or benefits processing), improve predictions (weather, disease, traffic), and engage constituents more effectively (via chatbots or recommendation engines). The result is more efficient operations and improved citizen satisfaction.
Government AI Use Cases
Governments around the world are deploying AI and algorithms to transform public services. For example, the Social Security Administration uses AI to streamline disability claim reviews, speeding up decisions and reducing backlogs. The Department of Labor has implemented AI chatbots to field citizen inquiries about unemployment benefits, allowing people to get answers at any time. In environmental monitoring, agencies like NASA collaborate with AI research teams to convert satellite data into maps that track climate and disaster risks. This helps predict floods or wildfires and inform emergency response.
Another example is fraud detection. Tax authorities use supervised learning models to flag suspicious tax returns that deviate from normal filing patterns. Customs and border agencies use AI models to identify security threats in cargo or passenger data. Even municipal governments use algorithms: San Jose’s chatbot (mentioned above) gave after-hours support to Spanish- and Vietnamese-speaking residents, collecting questions and thereby helping the city learn about the needs of communities often left out.
AI is also improving back-office functions in government. Machine learning can modernize legacy IT systems: for instance, the Office of Personnel Management plans to use AI to transform its old retirement systems and better serve federal retirees. In procurement, AI tools analyze vendor data to help agencies pick suppliers faster. In healthcare, health departments use AI to analyze public health data and detect early signs of outbreaks. In each case, algorithms are the engines behind intelligent applications whether image recognition, natural language processing, or predictive analytics that deliver these new capabilities.
Overall, these use cases show that AI algorithms are not just science fiction in government; they are practical tools embedded in government AI solutions. From customer-facing services (chatbots, mobile apps) to strategic analytics (predictive risk models), algorithms are woven into modern public sector IT. For example, federal platforms like USAi and OneGov provide secure environments where agencies can test government AI solutions (like document readers or citizen-service bots) before procurement. This underscores how fundamental algorithms are to the evolving digital government.
Challenges of AI in Government
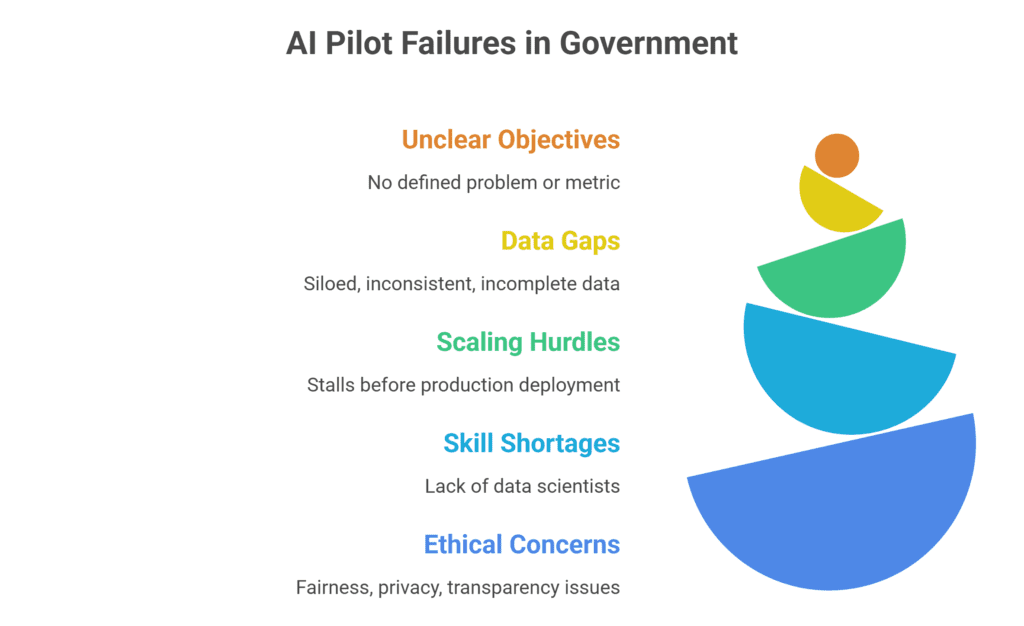
While the potential of AI is clear, Challenges of AI Pilots in government remain substantial. Experts estimate that a very high percentage of AI pilot projects fail to meet expectations. One analysis warns that about “95% of AI pilots fail to deliver expected returns,” often due to factors other than just the algorithm itself. The typical obstacles include:
- Unclear objectives and scope: Many pilots start without a well-defined problem or success metric. Without clear goals, even a powerful algorithm can miss the mark.
- Data and technology gaps: Government data is often siloed, inconsistent, or incomplete. Poor data quality and aging IT systems can undermine any AI model. In fact, ingesting bad data can make an AI tool reinforce inefficiencies rather than fix them.
- Scaling and adoption hurdles: It’s one thing to build a prototype and another to deploy at scale. Surveys show that over half of federal AI pilots stall before production due to issues like lack of budget, slow security approvals, or low user buy-in. If users aren’t engaged, a pilot may never gain traction.
- Workforce and skill shortages: Many agencies simply lack enough data scientists or machine learning engineers to sustain an AI project. Training is expensive and turnover can disrupt progress. This “people problem” often means projects fizzle out after the initial research phase.
- Ethical and governance concerns: Public agencies must be extra careful about fairness, privacy, and transparency. Strict regulations and public scrutiny mean any bias or opacity in an AI’s decision-making can halt a project. Hence, many pilots require elaborate review processes to ensure the AI is explainable and complies with the law.
These challenges highlight why the focus in government often starts with strong planning. Agencies are advised to define clear goals, invest in data governance, and engage stakeholders from the outset. Overcoming the hurdles typically requires a disciplined approach: cleaning and integrating data before modeling, running small focused pilots, and building governance frameworks (audit trails, ethics oversight) alongside the technology. As one App Maisters guide notes, pairing AI tools with process improvement and strategic planning is key to success.
Conclusion and Next Steps
AI algorithms are at the heart of modern public-sector innovation, but they only work when supported by solid data and strategy. In summary, how do AI algorithms work? They sift through data to find patterns, then apply statistical rules to make decisions and predictions, all while improving with feedback. There are various types of AI algorithms (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement, etc.) to match different government problems. Governments use these algorithms in countless ways from citizen-facing chatbots and fraud detectors to predictive analytics for healthcare and disaster response.
For public agencies and their technology leaders, the path forward is to embrace machine learning for government projects methodically. That means starting with pilot projects that address a clear mission need, ensuring clean data, and engaging experts who know both the technology and the public sector context. Strong collaboration with experienced partners can smooth this journey. As one leader notes, agencies benefit from working with an IT solutions provider that specializes in AI for the public sector, because they bring expertise in secure, compliant development.
To deliver on the promise of AI, officials must also stay updated on emerging tools and platforms, from certified cloud services to new government data-sharing initiatives. And they must keep citizen trust by using AI responsibly. The good news is that with careful planning and by leveraging proven practices like process analysis and phased scaling the odds of success improve dramatically.
Government agencies ready to explore these opportunities should consider partnering with experienced providers. Organizations like App Maisters offer government AI solutions and IT support tailored to public needs. By combining domain knowledge with cutting-edge AI algorithms, they help agencies modernize operations and deliver better digital services.
Take Action: If your agency is planning an AI or machine learning initiative, start by clarifying your goals and data strategy. Reach out to experts who understand federal technology requirements. With the right approach, how AI really works can translate into practical solutions from smarter chatbots and faster analytics to more efficient public services. Contact App Maisters or a trusted government IT partner today to discuss how AI can work for your agency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does an AI algorithm actually do?
An AI algorithm analyzes data to find patterns and make predictions without fixed rules. It learns from examples and improves its output over time.
What challenges should agencies expect when piloting AI?
Even well-designed pilots can fail without clear goals, clean data, or the right skills. Addressing these early boosts chances of success.
How do AI algorithms work with data?
AI algorithms take raw data, detect meaningful patterns, and adjust their internal settings through training. This lets them make smarter decisions with new inputs.
What are the main types of AI algorithms?
The main types of AI algorithms include supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning models, each suited for specific tasks like classification, clustering, or decision optimization.
Is machine learning the same as AI?
Machine learning is a core branch of AI. It refers to systems that learn patterns from data to make predictions, and it’s crucial for AI applications used by government agencies.
Why is machine learning for government important?
Machine learning for government helps automate processes, extract insights from large data sets, and boost service delivery efficiency in areas like public safety and citizen support.
How do AI algorithms improve over time?
AI models improve over time by learning from errors and new inputs. They adjust their rules based on feedback until they reach stable and accurate performance.






