

LLMOps (Large Language Model Operations) refers to the processes and tools for running advanced AI language models in production. It covers the full lifecycle of LLMs from preparing training data and fine‑tuning the model to deploying it, monitoring its output, and ensuring compliance. Essentially, think of LLMOps as MLOps on steroids for chatbots and other generative AI: it brings together data scientists, DevOps engineers and IT staff to handle data pipelines, model versioning, prompt engineering and performance tracking. By putting these workflows in place, agencies can make sure their AI applications run reliably, safely and at scale.
While LLMOps builds on the principles of MLOps, large language models introduce new challenges. LLMs are far larger and more complex than typical ML models training or fine-tuning them can involve billions of parameters and massive datasets. They also generate open‑ended text, so traditional accuracy metrics don’t tell the whole story. For example, LLMs often use metrics like BLEU or ROUGE for text quality, rather than simple accuracy. Moreover, running an LLM at scale usually requires specialized hardware (GPUs/TPUs) and careful cost management. In practice, LLMOps adds steps to the workflow that aren’t needed for smaller models: things like prompt and context management, retrieval‑augmented generation (RAG), continuous human‑in‑the‑loop feedback, and even chain-of-thought pipelines. As one guide summarizes, LLMOps handles scale, complexity, and ethical oversight at a level beyond classic MLOps.
For example, an LLMOps platform must track prompt versions and guard against hallucination (misinformation), which is far less of a concern for a fixed-output ML model. It must also support Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) using end-user corrections to fine-tune the model something rarely needed in ordinary ML. In short, LLMOps adapts the familiar CI/CD and monitoring pipelines of MLOps but adds governance, safety checks and scalability specifically for LLMs.
Governments are eager to tap generative AI to improve citizen services, data analysis and internal efficiency. In fact, surveys show public-sector tech leaders recognize the importance of AI: 64% say AI adoption is important, yet only about 26% have fully integrated AI in their organizations. This gap especially with only ~12% having adopted gen‑AI tools means agencies must move carefully and strategically. Successful AI adoption strategies in government hinge on strong governance, security and human oversight. Reports note that federal and state agencies are already expanding AI use to streamline services and decision-making, but unclear ethical frameworks (cited by 48% of leaders) and data infrastructure shortfalls (30%) are top barriers.
LLMOps public sector practices directly address these concerns. By baking in compliance and validation at every step, LLMOps ensures new AI services align with policies and regulations. For example, an LLMOps pipeline can enforce data encryption and privacy checks on all inputs, and require human review of sensitive outputs reflecting the ai governance human validation that agencies need. Similarly, monitoring tools within LLMOps watch for model drift or bias, so officials get alerts if the system begins to misbehave. These safeguards not only mitigate risk, they build trust. After all, public agencies must often justify AI results to oversight bodies. A robust LLMOps framework provides audit trails and reproducibility, making it easier to comply with mandates OMB and NIST guidance both emphasize transparency and accountability.
At the same time, LLMOps helps unlock AI’s benefits for the public sector. Well‑managed LLMs can turbocharge citizen services (e.g. virtual assistants and automated report generation), optimize workflows, and analyze data at scale all key parts of the broader public sector digital transformation. With proper operations, agencies can 24/7 human-like support citizens. For instance, a state revenue department launched an AI chatbot to answer tax and licensing questions anytime, drastically cutting citizen wait times. Another example: an environmental agency’s LLM‑powered agent automated permit review end-to-end, slashing processing time. These use cases wouldn’t be reliable without LLMOps pipelines behind them pipelines that track performance, version the model and data, and allow human editors to step in if needed.
Implementing LLMOps in a public agency means setting up a connected workflow. Key components include:
In summary, LLMOps weaves together data curation, model tuning, secure infrastructure and human oversight. It ensures that when an agency deploys an LLM in the field, it performs reliably, respects laws, and can be updated or shut down quickly if anything goes wrong.
With LLMOps in place, governments gain efficiency and risk control simultaneously.
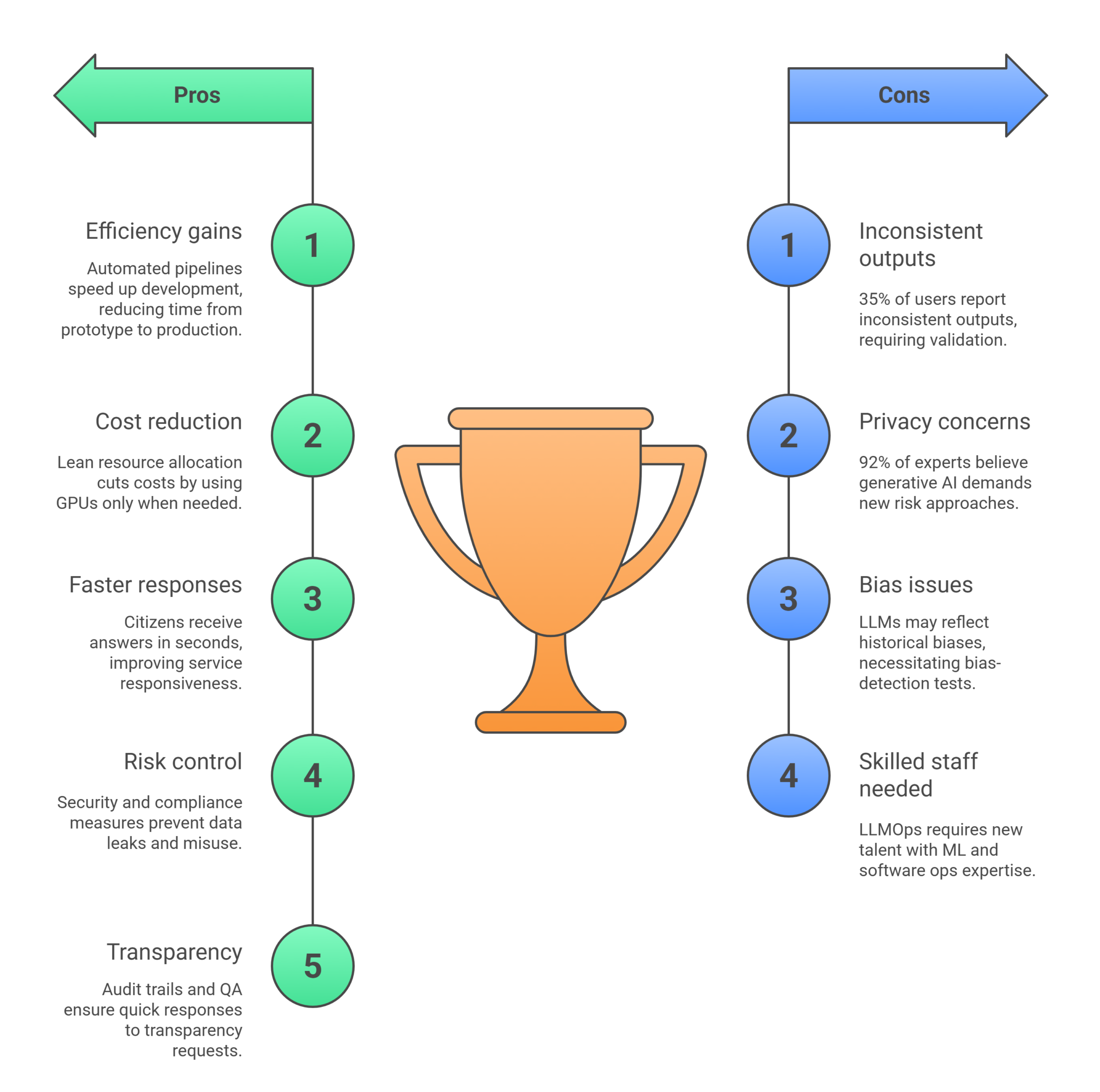
Consider these scenarios that illustrate LLMOps at work in government-like settings:
These examples show that no matter the task, LLMOps underpins success: it turns powerful but complex AI into practical tools that public servants and citizens can trust.
Large language models are reshaping how government can serve the public, but only if they’re managed properly. For public‑sector technology leaders, understanding and implementing LLMOps is now a strategic imperative. By embedding the right processes and tools essentially treating LLMs as production-critical systems agencies can reap AI’s benefits while meeting their unique accountability and security needs. Think of LLMOps as a key part of your government AI adoption strategies and public sector digital transformation roadmap.
If you’re ready to explore how LLMOps can work in your organization, consider our specialized artificial intelligence solutions for government. We can help you design an LLMOps framework with strong governance and human-in-the-loop safeguards. Embracing this approach now and even looking ahead to agentic AI public sector innovations will position your agency to deliver faster, smarter, and more reliable digital services to citizens.
LLMOps public sector focuses on managing, deploying, and monitoring large language models safely in government environments. It ensures compliance, security, and reliable AI outcomes for public services.
LLMOps government agencies rely on helps reduce risk, control costs, and improve service delivery. It also supports transparency, audits, and human oversight required in the public sector.
LLMOps vs MLOps differs mainly in scale and governance. LLMOps handles large models, prompt management, human validation, and ethical risks that standard MLOps does not fully address.
Deploying LLMs in government is safe when strong LLMOps practices are in place. This includes data security, access controls, bias checks, and continuous human review.
Common use cases include citizen chatbots, document analysis, policy summarization, and internal automation. All rely on LLMOps government agencies frameworks to stay compliant.
Yes. App Maisters delivers LLMOps public sector solutions designed for government agencies. Our services align with security, compliance, and public-sector operational needs.
Yes. With the right architecture, deploying LLMs in government can scale across agencies. LLMOps ensures consistent performance, governance, and monitoring at every level.
Commodo elementum, sed imperdiet nunc euismod etiam aliquet viverra

App Maisters Inc is a Federal Government SBA 8(a) Certified and Texas Hub Certified company. We are a leading developer of high-performance mobile apps, websites, and enterprise solutions, that are specially designed to meet Federal, State, Local government agencies and higher education needs.
